Protein Structure
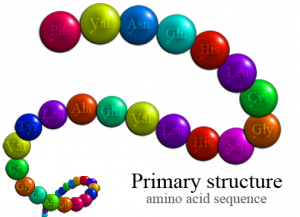
Primary Structure
The primary structure of a protein is its linear amino acid sequence.
Secondary Structure
The secondary structures of a protein refer to the ways in which local segments of its primary structure fold on themselves.
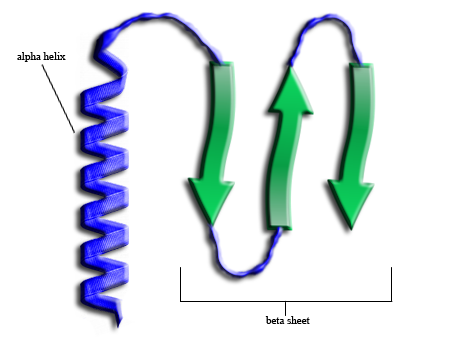
There are a variety of different secondary structural elements; the most common of these are alpha helices and beta sheets.
Alpha Helices
These right-handed helices are common motifs in protein secondary structure.
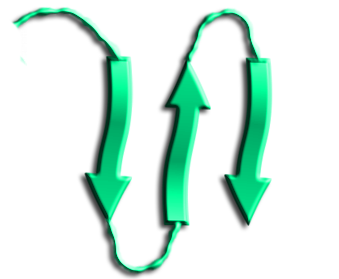
Beta Sheets
Beta sheets are pleated sheets consisting of beta strands laterally connected by at least 2-3 backbone hydrogen bonds.
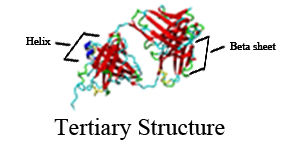
Tertiary Structure
The tertiary structures of a protein are the local three-dimensional shapes its secondary structure folds on itself to create.
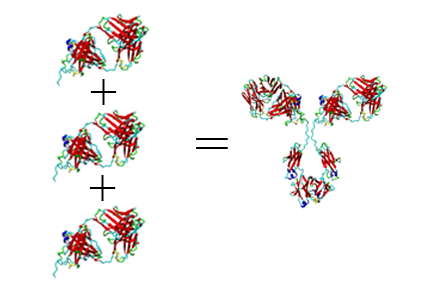
Quaternary Structure
Quaternary structure refers to the arrangement and number of multiple protein subunits comprising a multi-subunit complex.